Polynomial Long Division Mathbits Answers
In general you can skip the multiplication sign so 5 x is. Once you get to a remainder thats smaller in polynomial degree than the divisor youre done.

Polynomial Synthetic Division Mathbitsnotebook A2 Ccss Math Synthetic Division Ccss Math Polynomials
The former method is a great way to start using the app and then later you can start to type in your answers.
Polynomial long division mathbits answers. 2x4 0x3 4x2 0x - 1. We begin by dividing into the digits of the dividend that have the greatest place value. Multiply the denominator by that answer put that below the numerator.
Divide the term with the highest power inside the division symbol by the term with the highest power outside the division symbol. Divide the first term of the numerator by the first term of the denominator and put that in the answer. The object of this assignment is to find remainders.
Dividing Polynomials For problems 1 3 use long division to perform the indicated division. In this case we should get 2x 3 2x x 2 and x 2 2x 3. Subtract to create a new polynomial.
Finally subtract and bring down the next term. Chopping Polynomials Name_____ Directions. The same goes for polynomial long division.
We will be assuming that the divisors in these examples are not zero ie in Example 1 assume x - 3 0. Divide 3x4 5x2 3 3 x 4 5 x 2 3 by x2 x 2 Solution Divide x32x23x4 x 3 2 x 2 3 x 4 by x7 x 7 Solution. Polynomial Long Division In this lesson I will go over five 5 examples with detailed step-by-step solutions on how to divide polynomials using the long division method.
It is the generalised version of the familiar arithmetic technique called long division. As was done with long division synthetic division must also fill in missing terms in the dividend. If one of the integers is represented by x1 find expressions to represent the other two integers.
Once the remainder is discovered locate its accompanying letter value and decipher the hidden message about division at the end of this document. Use the root associated with the divisor. We divide multiply subtract include the digit in the next place value position and repeat.
Polynomial Long Division We are familiar with the long division algorithm for ordinary arithmetic. The product of three integers is represented by 3 2x32 xx. Here is the long division work for this problem.
It is very similar to what you did back in elementary when you try to divide large numbers for. It is easier to show with an example. Lets examine algebraic long division in a variety of situations.
For problems 1-8 find the remainder by long division. Repeat using the new polynomial. How could you describe these integers.
The Polynomial Long Division app has several settings that allow you to set the difficulty to suit your needs. Longdivisionfrac x 3x 2 x 2x-2 longdivisionfrac 4x 3-7x 2-11x5 4x5 longdivisionfrac 2x 25x-18 x4 polynomial-long-division-calculator. The determine the value of the coefficients p and q if the polynomial xpx qx32 12 is divisible by x2 23x.
The polynomial were dividing by has degree one and so in this case well stop when the remainder is degree zero ie. Sign in with Office365. Section 5-1.
You can either pick answers for each step from multiple choices or you can type in the answers yourself. Use a zero coefficient to hold the spot during the division process. Next multiply or distribute the answer obtained in the previous step by the polynomial in front of the division symbol.
Polynomial long division is an algorithm that implements the Euclidean division of polynomials which starting from two polynomials A the dividend and B the divisor produces if B is not zero a quotient Q and a remainder R such that A BQ R and either R 0 or the degree of R is lower than the degree of B. Let us take an example. The calculator will perform the long division of polynomials with steps shown.
Divide 2x3 9x2 15 by 2x 5. In algebra an algorithm for dividing a polynomial by another polynomial of the same or lower degree is called polynomial long division. Steps 2 3 and 4.
Polynomial Long Division Calculator. The 7 is just a constant term. The 3x is too big to go into it just like the 5 was too big to go into the 2 in the numerical long division example above.
X 2 9 x 60 x 7 x 3 2 x 2 3 x 4 x 3 7 x 2 9 x 2 3 x 4 9 x 2 63 x 60 x 4 60 x 420 424 x 2 9 x 60. 2x4 4x2 - 1 by x -1 Fill in missing terms. Checking answer with without a remainder.
Checking answer with without a remainder. Sign in with Facebook. This algorithm is simply saying that when the two polynomials are divided f x d x the solution will be the quotient q x plus a remainder expressed as the remainder over the divisor r x d x.
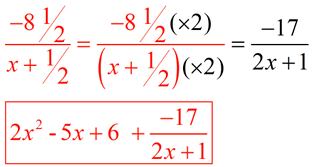
Polynomial Long Division And Synthetic Division Examples From Mathbits
Https Kippnashville Org Wp Content Uploads 2020 03 Algebra 2 Pdf

Step By Step How To Find Vertical Asymptotes Holes And Horizontal Asymptotes Using The Graphing Calculator Rational Function Math Methods Algebra

Dividing Polynomials By Linear Expressions Video Khan Academy
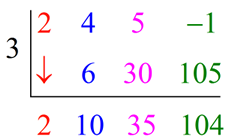
Polynomial Long Division And Synthetic Division Examples From Mathbits

57 Worksheet Piecewise Functions Algebra 2 Answers Pictures All About Worksheet Algebra Worksheets Quadratics Quadratic Functions

Inverse Functions Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math Inverse Functions Ccss Math Math Doodles

Pin By Maverick Hilgendorff On Math Precalculus Calculus Math Lessons
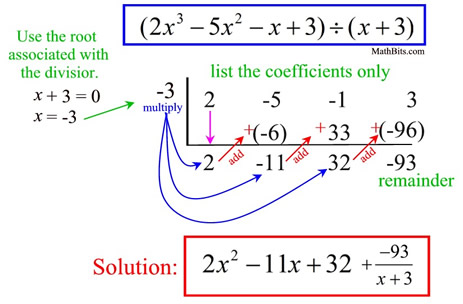
Howto How To Factor Polynomials With 4 Terms Synthetic Division
Http Hyman Weebly Com Uploads 1 3 4 3 13439681 Mathbits Polynomial Long Division Answers Pdf
Https Kippnashville Org Wp Content Uploads 2020 03 Algebra 2 Pdf
Https Kippnashville Org Wp Content Uploads 2020 03 Algebra 2 Pdf

Polynomial Synthetic Division Mathbitsnotebook A2 Ccss Math Ccss Math Polynomials Synthetic Division

Transformation Of A Cubic Function Cubic Function Precalculus Parent Functions
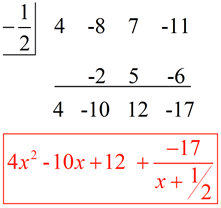
Polynomial Long Division And Synthetic Division Examples From Mathbits
Factoring Cubic Polynomials Worksheet Nidecmege
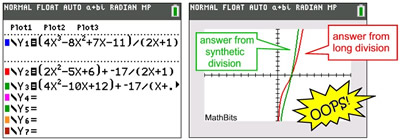
Polynomial Long Division And Synthetic Division Examples From Mathbits
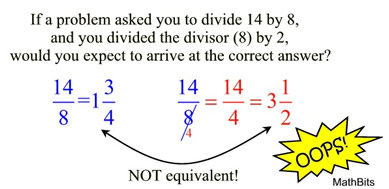
Polynomial Long Division And Synthetic Division Examples From Mathbits
